Crouzeix-Raviart elements are Navier-Stokes elements with quadratic interpolation for velocities and positions, but a discontinuous linear pressure interpolation. More...
#include <linearised_navier_stokes_elements.h>
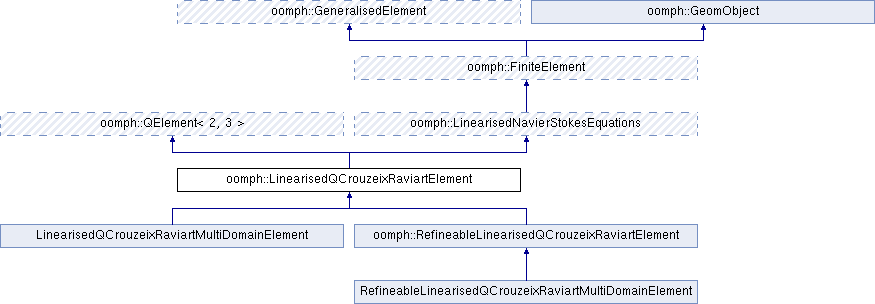
 Inheritance diagram for oomph::LinearisedQCrouzeixRaviartElement:
Inheritance diagram for oomph::LinearisedQCrouzeixRaviartElement:Public Member Functions | |
| LinearisedQCrouzeixRaviartElement () | |
| Constructor: there are three internal values for each of the two pressure components. | |
| virtual unsigned | required_nvalue (const unsigned &n) const |
| Return number of values (pinned or dofs) required at local node n. | |
| double | p_linearised_nst (const unsigned &i_internal, const unsigned &i) const |
| Return the pressure value i at internal dof i_internal (Discontinous pressure interpolation – no need to cater for hanging nodes) | |
| void | pin_pressure_normalisation_dofs () |
| Pin the normalisation dofs. | |
| void | pin_real_or_imag (const unsigned &real_index) |
| Pin the real or imaginary part of the problem Input integer 0 for real 1 for imaginary. | |
| void | unpin_real_or_imag (const unsigned &real_index) |
| void | copy_efunction_to_normalisation () |
| unsigned | npres_linearised_nst () const |
| Return number of pressure values corresponding to a single pressure component. | |
| void | fix_pressure (const unsigned &p_dof, const double &pvalue) |
| Fix both components of the internal pressure degrees of freedom p_dof to pvalue. | |
| int | p_local_eqn (const unsigned &n, const unsigned &i) |
| Overload the access function for the i-th component of the pressure's local equation numbers. | |
| void | output (std::ostream &outfile) |
| Redirect output to NavierStokesEquations output. | |
| void | output (std::ostream &outfile, const unsigned &n_plot) |
| Redirect output to NavierStokesEquations output. | |
| void | output (FILE *file_pt) |
| Redirect output to NavierStokesEquations output. | |
| void | output (FILE *file_pt, const unsigned &n_plot) |
| Redirect output to NavierStokesEquations output. | |
| unsigned | ndof_types () const |
| The number of "dof-blocks" that degrees of freedom in this element are sub-divided into: Velocity and pressure. | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from oomph::LinearisedNavierStokesEquations Public Member Functions inherited from oomph::LinearisedNavierStokesEquations | |
| LinearisedNavierStokesEquations () | |
| Constructor: NULL the base flow solution and the derivatives of the base flow function. | |
| const double & | re () const |
| Reynolds number. | |
| const double & | re_st () const |
| Product of Reynolds and Strouhal number (=Womersley number) | |
| const double & | lambda () const |
| const double & | omega () const |
| double *& | re_pt () |
| Pointer to Reynolds number. | |
| double *& | re_st_pt () |
| Pointer to product of Reynolds and Strouhal number (=Womersley number) | |
| double *& | lambda_pt () |
| Pointer to lambda. | |
| double *& | omega_pt () |
| Pointer to frequency. | |
| LinearisedNavierStokesEigenfunctionNormalisationElement * | normalisation_element_pt () |
| Pointer to normalisation element. | |
| void | set_eigenfunction_normalisation_element (LinearisedNavierStokesEigenfunctionNormalisationElement *const &normalisation_el_pt) |
| the boolean flag check_nodal_data is set to false. | |
| const double & | viscosity_ratio () const |
| Viscosity ratio for element: element's viscosity relative to the viscosity used in the definition of the Reynolds number. | |
| double *& | viscosity_ratio_pt () |
| Pointer to the viscosity ratio. | |
| const double & | density_ratio () const |
| Density ratio for element: element's density relative to the viscosity used in the definition of the Reynolds number. | |
| double *& | density_ratio_pt () |
| Pointer to the density ratio. | |
| virtual unsigned | u_index_linearised_nst (const unsigned &i) const |
| Return the index at which the i-th unknown velocity component is stored. The default value, i, is appropriate for single-physics problems. In derived multi-physics elements, this function should be overloaded to reflect the chosen storage scheme. Note that these equations require that the unknowns are always stored at the same indices at each node. | |
| double | du_dt_linearised_nst (const unsigned &n, const unsigned &i) const |
| Return the i-th component of du/dt at local node n. Uses suitably interpolated value for hanging nodes. | |
| void | disable_ALE () |
| Disable ALE, i.e. assert the mesh is not moving – you do this at your own risk! | |
| void | enable_ALE () |
| (Re-)enable ALE, i.e. take possible mesh motion into account when evaluating the time-derivative. Note: By default, ALE is enabled, at the expense of possibly creating unnecessary work in problems where the mesh is, in fact, stationary. | |
| virtual int | p_index_linearised_nst (const unsigned &i) const |
| Which nodal value represents the pressure? | |
| void | strain_rate (const Vector< double > &s, DenseMatrix< double > &strain_rate, const unsigned &real) const |
| Strain-rate tensor: | |
| void | output_veloc (std::ostream &outfile, const unsigned &nplot, const unsigned &t) |
| Output function: r, z, U^C, U^S, V^C, V^S, W^C, W^S, in tecplot format. nplot points in each coordinate direction at timestep t (t=0: present; t>0: previous timestep) | |
| void | fill_in_contribution_to_residuals (Vector< double > &residuals) |
| Compute the element's residual Vector. | |
| double | interpolated_u_linearised_nst (const Vector< double > &s, const unsigned &i) const |
| Compute the element's residual Vector and the jacobian matrix. Virtual function can be overloaded by hanging-node version. | |
| double | interpolated_p_linearised_nst (const Vector< double > &s, const unsigned &i) const |
| Return the i-th component of the FE interpolated pressure p[i] at local coordinate s. | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from oomph::FiniteElement Public Member Functions inherited from oomph::FiniteElement | |
| void | set_dimension (const unsigned &dim) |
| Set the dimension of the element and initially set the dimension of the nodes to be the same as the dimension of the element. | |
| void | set_nodal_dimension (const unsigned &nodal_dim) |
| Set the dimension of the nodes in the element. This will typically only be required when constructing FaceElements or in beam and shell type elements where a lower dimensional surface is embedded in a higher dimensional space. | |
| void | set_nnodal_position_type (const unsigned &nposition_type) |
| Set the number of types required to interpolate the coordinate. | |
| void | set_n_node (const unsigned &n) |
| Set the number of nodes in the element to n, by resizing the storage for pointers to the Node objects. | |
| int | nodal_local_eqn (const unsigned &n, const unsigned &i) const |
| Return the local equation number corresponding to the i-th value at the n-th local node. | |
| double | dJ_eulerian_at_knot (const unsigned &ipt, Shape &psi, DenseMatrix< double > &djacobian_dX) const |
| Compute the geometric shape functions (psi) at integration point ipt. Return the determinant of the jacobian of the mapping (detJ). Additionally calculate the derivatives of "detJ" w.r.t. the nodal coordinates. | |
| FiniteElement () | |
| Constructor. | |
| virtual | ~FiniteElement () |
| The destructor cleans up the static memory allocated for shape function storage. Internal and external data get wiped by the GeneralisedElement destructor; nodes get killed in mesh destructor. | |
| FiniteElement (const FiniteElement &)=delete | |
| Broken copy constructor. | |
| virtual bool | local_coord_is_valid (const Vector< double > &s) |
| Broken assignment operator. | |
| virtual void | move_local_coord_back_into_element (Vector< double > &s) const |
| Adjust local coordinates so that they're located inside the element. | |
| void | get_centre_of_gravity_and_max_radius_in_terms_of_zeta (Vector< double > &cog, double &max_radius) const |
| Compute centre of gravity of all nodes and radius of node that is furthest from it. Used to assess approximately if a point is likely to be contained with an element in locate_zeta-like operations. | |
| virtual void | local_coordinate_of_node (const unsigned &j, Vector< double > &s) const |
| Get local coordinates of node j in the element; vector sets its own size (broken virtual) | |
| virtual void | local_fraction_of_node (const unsigned &j, Vector< double > &s_fraction) |
| Get the local fraction of the node j in the element A dumb, but correct default implementation is provided. | |
| virtual double | local_one_d_fraction_of_node (const unsigned &n1d, const unsigned &i) |
| Get the local fraction of any node in the n-th position in a one dimensional expansion along the i-th local coordinate. | |
| virtual void | set_macro_elem_pt (MacroElement *macro_elem_pt) |
| Set pointer to macro element – can be overloaded in derived elements to perform additional tasks. | |
| MacroElement * | macro_elem_pt () |
| Access function to pointer to macro element. | |
| void | get_x (const Vector< double > &s, Vector< double > &x) const |
| Global coordinates as function of local coordinates. Either via FE representation or via macro-element (if Macro_elem_pt!=0) | |
| void | get_x (const unsigned &t, const Vector< double > &s, Vector< double > &x) |
| Global coordinates as function of local coordinates at previous time "level" t (t=0: present; t>0: previous). Either via FE representation of QElement or via macro-element (if Macro_elem_pt!=0). | |
| virtual void | get_x_from_macro_element (const Vector< double > &s, Vector< double > &x) const |
| Global coordinates as function of local coordinates using macro element representation. (Broken virtual — this must be overloaded in specific geometric element classes) | |
| virtual void | get_x_from_macro_element (const unsigned &t, const Vector< double > &s, Vector< double > &x) |
| Global coordinates as function of local coordinates at previous time "level" t (t=0: present; t>0: previous). using macro element representation (Broken virtual – overload in specific geometric element class if you want to use this functionality.) | |
| virtual void | set_integration_scheme (Integral *const &integral_pt) |
| Set the spatial integration scheme. | |
| Integral *const & | integral_pt () const |
| Return the pointer to the integration scheme (const version) | |
| virtual void | shape (const Vector< double > &s, Shape &psi) const =0 |
| Calculate the geometric shape functions at local coordinate s. This function must be overloaded for each specific geometric element. | |
| virtual void | shape_at_knot (const unsigned &ipt, Shape &psi) const |
| Return the geometric shape function at the ipt-th integration point. | |
| virtual void | dshape_local (const Vector< double > &s, Shape &psi, DShape &dpsids) const |
| Function to compute the geometric shape functions and derivatives w.r.t. local coordinates at local coordinate s. This function must be overloaded for each specific geometric element. (Broken virtual function — specifies the interface) | |
| virtual void | dshape_local_at_knot (const unsigned &ipt, Shape &psi, DShape &dpsids) const |
| Return the geometric shape function and its derivative w.r.t. the local coordinates at the ipt-th integration point. | |
| virtual void | d2shape_local (const Vector< double > &s, Shape &psi, DShape &dpsids, DShape &d2psids) const |
| Function to compute the geometric shape functions and also first and second derivatives w.r.t. local coordinates at local coordinate s. This function must be overloaded for each specific geometric element (if required). (Broken virtual function — specifies the interface). Numbering: 1D: d2psids(i,0) = | |
| virtual void | d2shape_local_at_knot (const unsigned &ipt, Shape &psi, DShape &dpsids, DShape &d2psids) const |
| Return the geometric shape function and its first and second derivatives w.r.t. the local coordinates at the ipt-th integration point. Numbering: 1D: d2psids(i,0) = | |
| virtual double | J_eulerian (const Vector< double > &s) const |
| Return the Jacobian of mapping from local to global coordinates at local position s. | |
| virtual double | J_eulerian_at_knot (const unsigned &ipt) const |
| Return the Jacobian of the mapping from local to global coordinates at the ipt-th integration point. | |
| void | check_J_eulerian_at_knots (bool &passed) const |
| Check that Jacobian of mapping between local and Eulerian coordinates at all integration points is positive. | |
| void | check_jacobian (const double &jacobian) const |
| Helper function used to check for singular or negative Jacobians in the transform from local to global or Lagrangian coordinates. | |
| double | dshape_eulerian (const Vector< double > &s, Shape &psi, DShape &dpsidx) const |
| Compute the geometric shape functions and also first derivatives w.r.t. global coordinates at local coordinate s; Returns Jacobian of mapping from global to local coordinates. | |
| virtual double | dshape_eulerian_at_knot (const unsigned &ipt, Shape &psi, DShape &dpsidx) const |
| Return the geometric shape functions and also first derivatives w.r.t. global coordinates at the ipt-th integration point. | |
| virtual double | dshape_eulerian_at_knot (const unsigned &ipt, Shape &psi, DShape &dpsi, DenseMatrix< double > &djacobian_dX, RankFourTensor< double > &d_dpsidx_dX) const |
| Compute the geometric shape functions (psi) and first derivatives w.r.t. global coordinates (dpsidx) at the ipt-th integration point. Return the determinant of the jacobian of the mapping (detJ). Additionally calculate the derivatives of both "detJ" and "dpsidx" w.r.t. the nodal coordinates. | |
| double | d2shape_eulerian (const Vector< double > &s, Shape &psi, DShape &dpsidx, DShape &d2psidx) const |
| Compute the geometric shape functions and also first and second derivatives w.r.t. global coordinates at local coordinate s; Returns Jacobian of mapping from global to local coordinates. Numbering: 1D: d2psidx(i,0) = | |
| virtual double | d2shape_eulerian_at_knot (const unsigned &ipt, Shape &psi, DShape &dpsidx, DShape &d2psidx) const |
| Return the geometric shape functions and also first and second derivatives w.r.t. global coordinates at ipt-th integration point. Numbering: 1D: d2psidx(i,0) = | |
| virtual void | assign_nodal_local_eqn_numbers (const bool &store_local_dof_pt) |
| Assign the local equation numbers for Data stored at the nodes Virtual so that it can be overloaded by RefineableFiniteElements. If the boolean is true then the pointers to the degrees of freedom associated with each equation number are stored in Dof_pt. | |
| virtual void | describe_local_dofs (std::ostream &out, const std::string ¤t_string) const |
| Function to describe the local dofs of the element[s]. The ostream specifies the output stream to which the description is written; the string stores the currently assembled output that is ultimately written to the output stream by Data::describe_dofs(...); it is typically built up incrementally as we descend through the call hierarchy of this function when called from Problem::describe_dofs(...) | |
| virtual void | describe_nodal_local_dofs (std::ostream &out, const std::string ¤t_string) const |
| Function to describe the local dofs of the element[s]. The ostream specifies the output stream to which the description is written; the string stores the currently assembled output that is ultimately written to the output stream by Data::describe_dofs(...); it is typically built up incrementally as we descend through the call hierarchy of this function when called from Problem::describe_dofs(...) | |
| virtual void | assign_all_generic_local_eqn_numbers (const bool &store_local_dof_pt) |
| Overloaded version of the calculation of the local equation numbers. If the boolean argument is true then pointers to the degrees of freedom associated with each equation number are stored locally in the array Dof_pt. | |
| Node *& | node_pt (const unsigned &n) |
| Return a pointer to the local node n. | |
| Node *const & | node_pt (const unsigned &n) const |
| Return a pointer to the local node n (const version) | |
| unsigned | nnode () const |
| Return the number of nodes. | |
| virtual unsigned | nnode_1d () const |
| Return the number of nodes along one edge of the element Default is to return zero — must be overloaded by geometric elements. | |
| double | raw_nodal_position (const unsigned &n, const unsigned &i) const |
| Return the i-th coordinate at local node n. Do not use the hanging node representation. NOTE: Moved to cc file because of a possible compiler bug in gcc (yes, really!). The move to the cc file avoids inlining which appears to cause problems (only) when compiled with gcc and -O3; offensive "illegal read" is in optimised-out section of code and data that is allegedly illegal is readily readable (by other means) just before this function is called so I can't really see how we could possibly be responsible for this... | |
| double | raw_nodal_position (const unsigned &t, const unsigned &n, const unsigned &i) const |
| Return the i-th coordinate at local node n, at time level t (t=0: present; t>0: previous time level). Do not use the hanging node representation. | |
| double | raw_dnodal_position_dt (const unsigned &n, const unsigned &i) const |
| Return the i-th component of nodal velocity: dx/dt at local node n. Do not use the hanging node representation. | |
| double | raw_dnodal_position_dt (const unsigned &n, const unsigned &j, const unsigned &i) const |
| Return the i-th component of j-th derivative of nodal position: d^jx/dt^j at node n. Do not use the hanging node representation. | |
| double | raw_nodal_position_gen (const unsigned &n, const unsigned &k, const unsigned &i) const |
| Return the value of the k-th type of the i-th positional variable at the local node n. Do not use the hanging node representation. | |
| double | raw_nodal_position_gen (const unsigned &t, const unsigned &n, const unsigned &k, const unsigned &i) const |
| Return the generalised nodal position (type k, i-th variable) at previous timesteps at local node n. Do not use the hanging node representation. | |
| double | raw_dnodal_position_gen_dt (const unsigned &n, const unsigned &k, const unsigned &i) const |
| i-th component of time derivative (velocity) of the generalised position, dx(k,i)/dt at local node n. ‘Type’: k; Coordinate direction: i. Do not use the hanging node representation. | |
| double | raw_dnodal_position_gen_dt (const unsigned &j, const unsigned &n, const unsigned &k, const unsigned &i) const |
| i-th component of j-th time derivative of the generalised position, dx(k,i)/dt at local node n. ‘Type’: k; Coordinate direction: i. Do not use the hanging node representation. | |
| double | nodal_position (const unsigned &n, const unsigned &i) const |
| Return the i-th coordinate at local node n. If the node is hanging, the appropriate interpolation is handled by the position function in the Node class. | |
| double | nodal_position (const unsigned &t, const unsigned &n, const unsigned &i) const |
| Return the i-th coordinate at local node n, at time level t (t=0: present; t>0: previous time level) Returns suitably interpolated version for hanging nodes. | |
| double | dnodal_position_dt (const unsigned &n, const unsigned &i) const |
| Return the i-th component of nodal velocity: dx/dt at local node n. | |
| double | dnodal_position_dt (const unsigned &n, const unsigned &j, const unsigned &i) const |
| Return the i-th component of j-th derivative of nodal position: d^jx/dt^j at node n. | |
| double | nodal_position_gen (const unsigned &n, const unsigned &k, const unsigned &i) const |
| Return the value of the k-th type of the i-th positional variable at the local node n. | |
| double | nodal_position_gen (const unsigned &t, const unsigned &n, const unsigned &k, const unsigned &i) const |
| Return the generalised nodal position (type k, i-th variable) at previous timesteps at local node n. | |
| double | dnodal_position_gen_dt (const unsigned &n, const unsigned &k, const unsigned &i) const |
| i-th component of time derivative (velocity) of the generalised position, dx(k,i)/dt at local node n. ‘Type’: k; Coordinate direction: i. | |
| double | dnodal_position_gen_dt (const unsigned &j, const unsigned &n, const unsigned &k, const unsigned &i) const |
| i-th component of j-th time derivative of the generalised position, dx(k,i)/dt at local node n. ‘Type’: k; Coordinate direction: i. | |
| virtual void | get_dresidual_dnodal_coordinates (RankThreeTensor< double > &dresidual_dnodal_coordinates) |
| Compute derivatives of elemental residual vector with respect to nodal coordinates. Default implementation by FD can be overwritten for specific elements. dresidual_dnodal_coordinates(l,i,j) = d res(l) / dX_{ij}. | |
| unsigned | nnodal_position_type () const |
| Return the number of coordinate types that the element requires to interpolate the geometry between the nodes. For Lagrange elements it is 1. | |
| bool | has_hanging_nodes () const |
| Return boolean to indicate if any of the element's nodes are geometrically hanging. | |
| unsigned | nodal_dimension () const |
| Return the required Eulerian dimension of the nodes in this element. | |
| virtual unsigned | nvertex_node () const |
| Return the number of vertex nodes in this element. Broken virtual function in "pure" finite elements. | |
| virtual Node * | vertex_node_pt (const unsigned &j) const |
| Pointer to the j-th vertex node in the element. Broken virtual function in "pure" finite elements. | |
| virtual Node * | construct_node (const unsigned &n) |
| Construct the local node n and return a pointer to the newly created node object. | |
| virtual Node * | construct_node (const unsigned &n, TimeStepper *const &time_stepper_pt) |
| Construct the local node n, including storage for history values required by timestepper, and return a pointer to the newly created node object. | |
| virtual Node * | construct_boundary_node (const unsigned &n) |
| Construct the local node n as a boundary node; that is a node that MAY be placed on a mesh boundary and return a pointer to the newly created node object. | |
| virtual Node * | construct_boundary_node (const unsigned &n, TimeStepper *const &time_stepper_pt) |
| Construct the local node n, including storage for history values required by timestepper, as a boundary node; that is a node that MAY be placed on a mesh boundary and return a pointer to the newly created node object. | |
| int | get_node_number (Node *const &node_pt) const |
| Return the number of the node *node_pt if this node is in the element, else return -1;. | |
| virtual Node * | get_node_at_local_coordinate (const Vector< double > &s) const |
| If there is a node at this local coordinate, return the pointer to the node. | |
| double | raw_nodal_value (const unsigned &n, const unsigned &i) const |
| Return the i-th value stored at local node n but do NOT take hanging nodes into account. | |
| double | raw_nodal_value (const unsigned &t, const unsigned &n, const unsigned &i) const |
| Return the i-th value stored at local node n, at time level t (t=0: present; t>0 previous timesteps), but do NOT take hanging nodes into account. | |
| double | nodal_value (const unsigned &n, const unsigned &i) const |
| Return the i-th value stored at local node n. Produces suitably interpolated values for hanging nodes. | |
| double | nodal_value (const unsigned &t, const unsigned &n, const unsigned &i) const |
| Return the i-th value stored at local node n, at time level t (t=0: present; t>0 previous timesteps). Produces suitably interpolated values for hanging nodes. | |
| unsigned | dim () const |
| Return the spatial dimension of the element, i.e. the number of local coordinates required to parametrise its geometry. | |
| virtual ElementGeometry::ElementGeometry | element_geometry () const |
| Return the geometry type of the element (either Q or T usually). | |
| virtual double | interpolated_x (const Vector< double > &s, const unsigned &i) const |
| Return FE interpolated coordinate x[i] at local coordinate s. | |
| virtual double | interpolated_x (const unsigned &t, const Vector< double > &s, const unsigned &i) const |
| Return FE interpolated coordinate x[i] at local coordinate s at previous timestep t (t=0: present; t>0: previous timestep) | |
| virtual void | interpolated_x (const Vector< double > &s, Vector< double > &x) const |
| Return FE interpolated position x[] at local coordinate s as Vector. | |
| virtual void | interpolated_x (const unsigned &t, const Vector< double > &s, Vector< double > &x) const |
| Return FE interpolated position x[] at local coordinate s at previous timestep t as Vector (t=0: present; t>0: previous timestep) | |
| virtual double | interpolated_dxdt (const Vector< double > &s, const unsigned &i, const unsigned &t) |
| Return t-th time-derivative of the i-th FE-interpolated Eulerian coordinate at local coordinate s. | |
| virtual void | interpolated_dxdt (const Vector< double > &s, const unsigned &t, Vector< double > &dxdt) |
| Compte t-th time-derivative of the FE-interpolated Eulerian coordinate vector at local coordinate s. | |
| unsigned | ngeom_data () const |
| A standard FiniteElement is fixed, so there are no geometric data when viewed in its GeomObject incarnation. | |
| Data * | geom_data_pt (const unsigned &j) |
| A standard FiniteElement is fixed, so there are no geometric data when viewed in its GeomObject incarnation. | |
| void | position (const Vector< double > &zeta, Vector< double > &r) const |
| Return the parametrised position of the FiniteElement in its incarnation as a GeomObject, r(zeta). The position is given by the Eulerian coordinate and the intrinsic coordinate (zeta) is the local coordinate of the element (s). | |
| void | position (const unsigned &t, const Vector< double > &zeta, Vector< double > &r) const |
| Return the parametrised position of the FiniteElement in its GeomObject incarnation: r(zeta). The position is given by the Eulerian coordinate and the intrinsic coordinate (zeta) is the local coordinate of the element (s) This version of the function returns the position as a function of time t=0: current time; t>0: previous timestep. Works for t=0 but needs to be overloaded if genuine time-dependence is required. | |
| void | dposition_dt (const Vector< double > &zeta, const unsigned &t, Vector< double > &drdt) |
| Return the t-th time derivative of the parametrised position of the FiniteElement in its GeomObject incarnation: | |
| virtual double | zeta_nodal (const unsigned &n, const unsigned &k, const unsigned &i) const |
| Specify the values of the "global" intrinsic coordinate, zeta, of a compound geometric object (a mesh of elements) when the element is viewied as a sub-geometric object. The default assumption is that the element will be treated as a sub-geometric object in a bulk Mesh of other elements (geometric objects). The "global" coordinate of the compound geometric object is simply the Eulerian coordinate, x. The second default assumption is that the coordinate zeta will be stored at the nodes and interpolated using the shape functions of the element. This function returns the value of zeta stored at local node n, where k is the type of coordinate and i is the coordinate direction. The function is virtual so that it can be overloaded by different types of element: FaceElements and SolidFiniteElements. | |
| void | interpolated_zeta (const Vector< double > &s, Vector< double > &zeta) const |
| Calculate the interpolated value of zeta, the intrinsic coordinate of the element when viewed as a compound geometric object within a Mesh as a function of the local coordinate of the element, s. The default assumption is the zeta is interpolated using the shape functions of the element with the values given by zeta_nodal(). A MacroElement representation of the intrinsic coordinate parametrised by the local coordinate s is used if available. Choosing the MacroElement representation of zeta (Eulerian x by default) allows a correspondence to be established between elements on different Meshes covering the same curvilinear domain in cases where one element is much coarser than the other. | |
| void | locate_zeta (const Vector< double > &zeta, GeomObject *&geom_object_pt, Vector< double > &s, const bool &use_coordinate_as_initial_guess=false) |
| For a given value of zeta, the "global" intrinsic coordinate of a mesh of FiniteElements represented as a compound geometric object, find the local coordinate in this element that corresponds to the requested value of zeta. If zeta cannot be located in this element, geom_object_pt is set to NULL. If zeta is located in this element, we return its "this" pointer. By default don't use any value passed in to the local coordinate s as the initial guess in the Newton method. | |
| virtual void | node_update () |
| Update the positions of all nodes in the element using each node update function. The default implementation may be overloaded so that more efficient versions can be written. | |
| virtual void | identify_field_data_for_interactions (std::set< std::pair< Data *, unsigned > > &paired_field_data) |
The purpose of this function is to identify all possible Data that can affect the fields interpolated by the FiniteElement. The information will typically be used in interaction problems in which the FiniteElement provides a forcing term for an ElementWithExternalElement. The Data must be provided as paired_load data containing. | |
| virtual void | identify_geometric_data (std::set< Data * > &geometric_data_pt) |
The purpose of this function is to identify all Data objects that affect the elements' geometry. This function is implemented as an empty virtual function since it can only be implemented in conjunction with a node-update strategy. A specific implementation is provided in the ElementWithMovingNodes class. | |
| virtual double | s_min () const |
| Min value of local coordinate. | |
| virtual double | s_max () const |
| Max. value of local coordinate. | |
| double | size () const |
| Calculate the size of the element (length, area, volume,...) in Eulerian computational coordinates. Use suitably overloaded compute_physical_size() function to compute the actual size (taking into account factors such as 2pi or radii the integrand) – such function can only be implemented on an equation-by-equation basis. | |
| virtual double | compute_physical_size () const |
| Broken virtual function to compute the actual size (taking into account factors such as 2pi or radii the integrand) – such function can only be implemented on an equation-by-equation basis. | |
| virtual void | point_output_data (const Vector< double > &s, Vector< double > &data) |
| Virtual function to write the double precision numbers that appear in a single line of output into the data vector. Empty virtual, can be overloaded for specific elements; used e.g. by LineVisualiser. | |
| void | point_output (std::ostream &outfile, const Vector< double > &s) |
| Output solution (as defined by point_output_data()) at local cordinates s. | |
| virtual unsigned | nplot_points_paraview (const unsigned &nplot) const |
| Return the number of actual plot points for paraview plot with parameter nplot. Broken virtual; can be overloaded in specific elements. | |
| virtual unsigned | nsub_elements_paraview (const unsigned &nplot) const |
| Return the number of local sub-elements for paraview plot with parameter nplot. Broken virtual; can be overloaded in specific elements. | |
| void | output_paraview (std::ofstream &file_out, const unsigned &nplot) const |
| Paraview output – this outputs the coordinates at the plot points (for parameter nplot) to specified output file. | |
| virtual void | write_paraview_output_offset_information (std::ofstream &file_out, const unsigned &nplot, unsigned &counter) const |
| Fill in the offset information for paraview plot. Broken virtual. Needs to be implemented for each new geometric element type; see http://www.vtk.org/VTK/img/file-formats.pdf. | |
| virtual void | write_paraview_type (std::ofstream &file_out, const unsigned &nplot) const |
| Return the paraview element type. Broken virtual. Needs to be implemented for each new geometric element type; see http://www.vtk.org/VTK/img/file-formats.pdf. | |
| virtual void | write_paraview_offsets (std::ofstream &file_out, const unsigned &nplot, unsigned &offset_sum) const |
| Return the offsets for the paraview sub-elements. Broken virtual. Needs to be implemented for each new geometric element type; see http://www.vtk.org/VTK/img/file-formats.pdf. | |
| virtual unsigned | nscalar_paraview () const |
| Number of scalars/fields output by this element. Broken virtual. Needs to be implemented for each new specific element type. | |
| virtual void | scalar_value_paraview (std::ofstream &file_out, const unsigned &i, const unsigned &nplot) const |
| Write values of the i-th scalar field at the plot points. Broken virtual. Needs to be implemented for each new specific element type. | |
| virtual void | scalar_value_fct_paraview (std::ofstream &file_out, const unsigned &i, const unsigned &nplot, FiniteElement::SteadyExactSolutionFctPt exact_soln_pt) const |
| Write values of the i-th scalar field at the plot points. Broken virtual. Needs to be implemented for each new specific element type. | |
| virtual void | scalar_value_fct_paraview (std::ofstream &file_out, const unsigned &i, const unsigned &nplot, const double &time, FiniteElement::UnsteadyExactSolutionFctPt exact_soln_pt) const |
| Write values of the i-th scalar field at the plot points. Broken virtual. Needs to be implemented for each new specific element type. | |
| virtual std::string | scalar_name_paraview (const unsigned &i) const |
| Name of the i-th scalar field. Default implementation returns V1 for the first one, V2 for the second etc. Can (should!) be overloaded with more meaningful names in specific elements. | |
| virtual void | output (const unsigned &t, std::ostream &outfile, const unsigned &n_plot) const |
| Output the element data at time step t. This is const because it is newly added and so can be done easily. Really all the output(...) functions should be const! | |
| virtual void | output_fct (std::ostream &outfile, const unsigned &n_plot, FiniteElement::SteadyExactSolutionFctPt exact_soln_pt) |
| Output an exact solution over the element. | |
| virtual void | output_fct (std::ostream &outfile, const unsigned &n_plot, const double &time, FiniteElement::UnsteadyExactSolutionFctPt exact_soln_pt) |
| Output a time-dependent exact solution over the element. | |
| virtual void | output_fct (std::ostream &outfile, const unsigned &n_plot, const double &time, const SolutionFunctorBase &exact_soln) const |
| Output a time-dependent exact solution over the element. | |
| virtual void | get_s_plot (const unsigned &i, const unsigned &nplot, Vector< double > &s, const bool &shifted_to_interior=false) const |
| Get cector of local coordinates of plot point i (when plotting nplot points in each "coordinate direction"). Generally these plot points will be uniformly spaced across the element. The optional final boolean flag (default: false) allows them to be shifted inwards to avoid duplication of plot point points between elements – useful when they are used in locate_zeta, say. | |
| virtual std::string | tecplot_zone_string (const unsigned &nplot) const |
| Return string for tecplot zone header (when plotting nplot points in each "coordinate direction") | |
| virtual void | write_tecplot_zone_footer (std::ostream &outfile, const unsigned &nplot) const |
| Add tecplot zone "footer" to output stream (when plotting nplot points in each "coordinate direction"). Empty by default – can be used, e.g., to add FE connectivity lists to elements that need it. | |
| virtual void | write_tecplot_zone_footer (FILE *file_pt, const unsigned &nplot) const |
| Add tecplot zone "footer" to C-style output. (when plotting nplot points in each "coordinate direction"). Empty by default – can be used, e.g., to add FE connectivity lists to elements that need it. | |
| virtual unsigned | nplot_points (const unsigned &nplot) const |
| Return total number of plot points (when plotting nplot points in each "coordinate direction") | |
| virtual void | compute_error (FiniteElement::SteadyExactSolutionFctPt exact_soln_pt, double &error, double &norm) |
| Calculate the norm of the error and that of the exact solution. | |
| virtual void | compute_error (FiniteElement::UnsteadyExactSolutionFctPt exact_soln_pt, const double &time, double &error, double &norm) |
| Calculate the norm of the error and that of the exact solution. | |
| virtual void | compute_error (FiniteElement::SteadyExactSolutionFctPt exact_soln_pt, Vector< double > &error, Vector< double > &norm) |
| Given the exact solution | |
| virtual void | compute_error (FiniteElement::UnsteadyExactSolutionFctPt exact_soln_pt, const double &time, Vector< double > &error, Vector< double > &norm) |
| Given the exact solution | |
| virtual void | compute_error (std::ostream &outfile, FiniteElement::SteadyExactSolutionFctPt exact_soln_pt, double &error, double &norm) |
| Plot the error when compared against a given exact solution | |
| virtual void | compute_error (std::ostream &outfile, FiniteElement::UnsteadyExactSolutionFctPt exact_soln_pt, const double &time, double &error, double &norm) |
| Plot the error when compared against a given time-dependent exact solution | |
| virtual void | compute_error (std::ostream &outfile, FiniteElement::SteadyExactSolutionFctPt exact_soln_pt, Vector< double > &error, Vector< double > &norm) |
| Plot the error when compared against a given exact solution | |
| virtual void | compute_error (std::ostream &outfile, FiniteElement::UnsteadyExactSolutionFctPt exact_soln_pt, const double &time, Vector< double > &error, Vector< double > &norm) |
| Plot the error when compared against a given time-dependent exact solution | |
| virtual void | compute_abs_error (std::ostream &outfile, FiniteElement::SteadyExactSolutionFctPt exact_soln_pt, double &error) |
| Plot the error when compared against a given exact solution | |
| void | integrate_fct (FiniteElement::SteadyExactSolutionFctPt integrand_fct_pt, Vector< double > &integral) |
| Evaluate integral of a Vector-valued function | |
| void | integrate_fct (FiniteElement::UnsteadyExactSolutionFctPt integrand_fct_pt, const double &time, Vector< double > &integral) |
| Evaluate integral of a Vector-valued, time-dependent function | |
| virtual void | build_face_element (const int &face_index, FaceElement *face_element_pt) |
| Function for building a lower dimensional FaceElement on the specified face of the FiniteElement. The arguments are the index of the face, an integer whose value depends on the particular element type, and a pointer to the FaceElement. | |
| virtual unsigned | self_test () |
| Self-test: Check inversion of element & do self-test for GeneralisedElement. Return 0 if OK. | |
| virtual unsigned | get_bulk_node_number (const int &face_index, const unsigned &i) const |
| Get the number of the ith node on face face_index (in the bulk node vector). | |
| virtual int | face_outer_unit_normal_sign (const int &face_index) const |
| Get the sign of the outer unit normal on the face given by face_index. | |
| virtual unsigned | nnode_on_face () const |
| void | face_node_number_error_check (const unsigned &i) const |
| Range check for face node numbers. | |
| virtual CoordinateMappingFctPt | face_to_bulk_coordinate_fct_pt (const int &face_index) const |
| Get a pointer to the function mapping face coordinates to bulk coordinates. | |
| virtual BulkCoordinateDerivativesFctPt | bulk_coordinate_derivatives_fct_pt (const int &face_index) const |
| Get a pointer to the derivative of the mapping from face to bulk coordinates. | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from oomph::GeneralisedElement Public Member Functions inherited from oomph::GeneralisedElement | |
| virtual | ~GeneralisedElement () |
| Virtual destructor to clean up any memory allocated by the object. | |
| GeneralisedElement (const GeneralisedElement &)=delete | |
| Broken copy constructor. | |
| void | operator= (const GeneralisedElement &)=delete |
| Broken assignment operator. | |
| Data *& | internal_data_pt (const unsigned &i) |
| Return a pointer to i-th internal data object. | |
| Data *const & | internal_data_pt (const unsigned &i) const |
| Return a pointer to i-th internal data object (const version) | |
| Data *& | external_data_pt (const unsigned &i) |
| Return a pointer to i-th external data object. | |
| Data *const & | external_data_pt (const unsigned &i) const |
| Return a pointer to i-th external data object (const version) | |
| unsigned long | eqn_number (const unsigned &ieqn_local) const |
| Return the global equation number corresponding to the ieqn_local-th local equation number. | |
| int | local_eqn_number (const unsigned long &ieqn_global) const |
| Return the local equation number corresponding to the ieqn_global-th global equation number. Returns minus one (-1) if there is no local degree of freedom corresponding to the chosen global equation number. | |
| unsigned | add_external_data (Data *const &data_pt, const bool &fd=true) |
Add a (pointer to an) external data object to the element and return its index (i.e. the index required to obtain it from the access function external_data_pt(...). The optional boolean flag indicates whether the data should be included in the general finite-difference loop when calculating the jacobian. The default value is true, i.e. the data will be included in the finite-differencing. | |
| bool | external_data_fd (const unsigned &i) const |
| Return the status of the boolean flag indicating whether the external data is included in the finite difference loop. | |
| void | exclude_external_data_fd (const unsigned &i) |
| Set the boolean flag to exclude the external datum from the the finite difference loop when computing the jacobian matrix. | |
| void | include_external_data_fd (const unsigned &i) |
| Set the boolean flag to include the external datum in the the finite difference loop when computing the jacobian matrix. | |
| void | flush_external_data () |
| Flush all external data. | |
| void | flush_external_data (Data *const &data_pt) |
| Flush the object addressed by data_pt from the external data array. | |
| unsigned | ninternal_data () const |
| Return the number of internal data objects. | |
| unsigned | nexternal_data () const |
| Return the number of external data objects. | |
| unsigned | ndof () const |
| Return the number of equations/dofs in the element. | |
| void | dof_vector (const unsigned &t, Vector< double > &dof) |
| Return the vector of dof values at time level t. | |
| void | dof_pt_vector (Vector< double * > &dof_pt) |
| Return the vector of pointers to dof values. | |
| void | set_internal_data_time_stepper (const unsigned &i, TimeStepper *const &time_stepper_pt, const bool &preserve_existing_data) |
| Set the timestepper associated with the i-th internal data object. | |
| void | assign_internal_eqn_numbers (unsigned long &global_number, Vector< double * > &Dof_pt) |
| Assign the global equation numbers to the internal Data. The arguments are the current highest global equation number (which will be incremented) and a Vector of pointers to the global variables (to which any unpinned values in the internal Data are added). | |
| void | describe_dofs (std::ostream &out, const std::string ¤t_string) const |
| Function to describe the dofs of the element. The ostream specifies the output stream to which the description is written; the string stores the currently assembled output that is ultimately written to the output stream by Data::describe_dofs(...); it is typically built up incrementally as we descend through the call hierarchy of this function when called from Problem::describe_dofs(...) | |
| void | add_internal_value_pt_to_map (std::map< unsigned, double * > &map_of_value_pt) |
| Add pointers to the internal data values to map indexed by the global equation number. | |
| void | add_internal_data_values_to_vector (Vector< double > &vector_of_values) |
| Add all internal data and time history values to the vector in the internal storage order. | |
| void | read_internal_data_values_from_vector (const Vector< double > &vector_of_values, unsigned &index) |
| Read all internal data and time history values from the vector starting from index. On return the index will be set to the value at the end of the data that has been read in. | |
| void | add_internal_eqn_numbers_to_vector (Vector< long > &vector_of_eqn_numbers) |
| Add all equation numbers associated with internal data to the vector in the internal storage order. | |
| void | read_internal_eqn_numbers_from_vector (const Vector< long > &vector_of_eqn_numbers, unsigned &index) |
| Read all equation numbers associated with internal data from the vector starting from index. On return the index will be set to the value at the end of the data that has been read in. | |
| virtual void | assign_local_eqn_numbers (const bool &store_local_dof_pt) |
| Setup the arrays of local equation numbers for the element. If the optional boolean argument is true, then pointers to the associated degrees of freedom are stored locally in the array Dof_pt. | |
| virtual void | complete_setup_of_dependencies () |
| Complete the setup of any additional dependencies that the element may have. Empty virtual function that may be overloaded for specific derived elements. Used, e.g., for elements with algebraic node update functions to determine the "geometric
Data", i.e. the Data that affects the element's shape. This function is called (for all elements) at the very beginning of the equation numbering procedure to ensure that all dependencies are accounted for. | |
| virtual void | get_residuals (Vector< double > &residuals) |
| Calculate the vector of residuals of the equations in the element. By default initialise the vector to zero and then call the fill_in_contribution_to_residuals() function. Note that this entire function can be overloaded if desired. | |
| virtual void | get_jacobian (Vector< double > &residuals, DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian) |
| Calculate the elemental Jacobian matrix "d equation / d
variable". | |
| virtual void | get_mass_matrix (Vector< double > &residuals, DenseMatrix< double > &mass_matrix) |
| Calculate the residuals and the elemental "mass" matrix, the matrix that multiplies the time derivative terms in a problem. | |
| virtual void | get_jacobian_and_mass_matrix (Vector< double > &residuals, DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, DenseMatrix< double > &mass_matrix) |
| Calculate the residuals and jacobian and elemental "mass" matrix, the matrix that multiplies the time derivative terms. | |
| virtual void | get_dresiduals_dparameter (double *const ¶meter_pt, Vector< double > &dres_dparam) |
| Calculate the derivatives of the residuals with respect to a parameter. | |
| virtual void | get_djacobian_dparameter (double *const ¶meter_pt, Vector< double > &dres_dparam, DenseMatrix< double > &djac_dparam) |
| Calculate the derivatives of the elemental Jacobian matrix and residuals with respect to a parameter. | |
| virtual void | get_djacobian_and_dmass_matrix_dparameter (double *const ¶meter_pt, Vector< double > &dres_dparam, DenseMatrix< double > &djac_dparam, DenseMatrix< double > &dmass_matrix_dparam) |
| Calculate the derivatives of the elemental Jacobian matrix mass matrix and residuals with respect to a parameter. | |
| virtual void | get_hessian_vector_products (Vector< double > const &Y, DenseMatrix< double > const &C, DenseMatrix< double > &product) |
| Calculate the product of the Hessian (derivative of Jacobian with respect to all variables) an eigenvector, Y, and other specified vectors, C (d(J_{ij})/d u_{k}) Y_{j} C_{k}. | |
| virtual void | get_inner_products (Vector< std::pair< unsigned, unsigned > > const &history_index, Vector< double > &inner_product) |
| Return the vector of inner product of the given pairs of history values. | |
| virtual void | get_inner_product_vectors (Vector< unsigned > const &history_index, Vector< Vector< double > > &inner_product_vector) |
| Compute the vectors that when taken as a dot product with other history values give the inner product over the element. | |
| virtual void | compute_norm (Vector< double > &norm) |
| Compute norm of solution – broken virtual can be overloaded by element writer to implement whatever norm is desired for the specific element. | |
| virtual void | compute_norm (double &norm) |
| Compute norm of solution – broken virtual can be overloaded by element writer to implement whatever norm is desired for the specific element. | |
| void | set_halo (const unsigned &non_halo_proc_ID) |
| Label the element as halo and specify processor that holds non-halo counterpart. | |
| void | set_nonhalo () |
| Label the element as not being a halo. | |
| bool | is_halo () const |
| Is this element a halo? | |
| int | non_halo_proc_ID () |
| ID of processor ID that holds non-halo counterpart of halo element; negative if not a halo. | |
| void | set_must_be_kept_as_halo () |
| Insist that this element be kept as a halo element during a distribute? | |
| void | unset_must_be_kept_as_halo () |
| Do not insist that this element be kept as a halo element during distribution. | |
| bool | must_be_kept_as_halo () const |
| Test whether the element must be kept as a halo element. | |
| virtual void | get_dof_numbers_for_unknowns (std::list< std::pair< unsigned long, unsigned > > &dof_lookup_list) const |
Create a list of pairs for the unknowns that this element is "in charge of" – ignore any unknowns associated with external Data. The first entry in each pair must contain the global equation number of the unknown, while the second one contains the number of the DOF type that this unknown is associated with. (The function can obviously only be called if the equation numbering scheme has been set up.) | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from oomph::GeomObject Public Member Functions inherited from oomph::GeomObject | |
| GeomObject () | |
| Default constructor. | |
| GeomObject (const unsigned &ndim) | |
| Constructor: Pass dimension of geometric object (# of Eulerian coords = # of Lagrangian coords; no time history available/needed) | |
| GeomObject (const unsigned &nlagrangian, const unsigned &ndim) | |
| Constructor: pass # of Eulerian and Lagrangian coordinates. No time history available/needed. | |
| GeomObject (const unsigned &nlagrangian, const unsigned &ndim, TimeStepper *time_stepper_pt) | |
| Constructor: pass # of Eulerian and Lagrangian coordinates and pointer to time-stepper which is used to handle the position at previous timesteps and allows the evaluation of veloc/acceleration etc. in cases where the GeomData varies with time. | |
| GeomObject (const GeomObject &dummy)=delete | |
| Broken copy constructor. | |
| void | operator= (const GeomObject &)=delete |
| Broken assignment operator. | |
| virtual | ~GeomObject () |
| (Empty) destructor | |
| unsigned | nlagrangian () const |
| Access function to # of Lagrangian coordinates. | |
| unsigned | ndim () const |
| Access function to # of Eulerian coordinates. | |
| void | set_nlagrangian_and_ndim (const unsigned &n_lagrangian, const unsigned &n_dim) |
| Set # of Lagrangian and Eulerian coordinates. | |
| TimeStepper *& | time_stepper_pt () |
| Access function for pointer to time stepper: Null if object is not time-dependent. | |
| TimeStepper * | time_stepper_pt () const |
| Access function for pointer to time stepper: Null if object is not time-dependent. Const version. | |
| virtual void | position (const double &t, const Vector< double > &zeta, Vector< double > &r) const |
| Parametrised position on object: r(zeta). Evaluated at the continuous time value, t. | |
| virtual void | dposition (const Vector< double > &zeta, DenseMatrix< double > &drdzeta) const |
| Derivative of position Vector w.r.t. to coordinates: | |
| virtual void | d2position (const Vector< double > &zeta, RankThreeTensor< double > &ddrdzeta) const |
| 2nd derivative of position Vector w.r.t. to coordinates: | |
| virtual void | d2position (const Vector< double > &zeta, Vector< double > &r, DenseMatrix< double > &drdzeta, RankThreeTensor< double > &ddrdzeta) const |
| Posn Vector and its 1st & 2nd derivatives w.r.t. to coordinates: | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| double | dshape_and_dtest_eulerian_linearised_nst (const Vector< double > &s, Shape &psi, DShape &dpsidx, Shape &test, DShape &dtestdx) const |
| Velocity shape and test functions and their derivatives w.r.t. global coordinates at local coordinate s (taken from geometry). Return Jacobian of mapping between local and global coordinates. | |
| double | dshape_and_dtest_eulerian_at_knot_linearised_nst (const unsigned &ipt, Shape &psi, DShape &dpsidx, Shape &test, DShape &dtestdx) const |
| Velocity shape and test functions and their derivatives w.r.t. global coordinates at the ipt-th integation point (taken from geometry). Return Jacobian of mapping between local and global coordinates. | |
| void | pshape_linearised_nst (const Vector< double > &s, Shape &psi) const |
| Compute the pressure shape functions at local coordinate s. | |
| void | pshape_linearised_nst (const Vector< double > &s, Shape &psi, Shape &test) const |
| Compute the pressure shape and test functions at local coordinate s. | |
 Protected Member Functions inherited from oomph::LinearisedNavierStokesEquations Protected Member Functions inherited from oomph::LinearisedNavierStokesEquations | |
| virtual void | get_base_flow_u (const double &time, const unsigned &ipt, const Vector< double > &x, Vector< double > &result) const |
| Calculate the velocity components of the base flow solution at a given time and Eulerian position. | |
| virtual void | get_base_flow_dudx (const double &time, const unsigned &ipt, const Vector< double > &x, DenseMatrix< double > &result) const |
| Calculate the derivatives of the velocity components of the base flow solution w.r.t. global coordinates (r and z) at a given time and Eulerian position. | |
| int | eigenvalue_local_eqn (const unsigned &i) |
| virtual void | fill_in_generic_residual_contribution_linearised_nst (Vector< double > &residuals, DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, DenseMatrix< double > &mass_matrix, unsigned flag) |
| Compute the residuals for the Navier-Stokes equations; flag=1(or 0): do (or don't) compute the Jacobian as well. | |
 Protected Member Functions inherited from oomph::FiniteElement Protected Member Functions inherited from oomph::FiniteElement | |
| virtual void | assemble_local_to_eulerian_jacobian (const DShape &dpsids, DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian) const |
| Assemble the jacobian matrix for the mapping from local to Eulerian coordinates, given the derivatives of the shape function w.r.t the local coordinates. | |
| virtual void | assemble_local_to_eulerian_jacobian2 (const DShape &d2psids, DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian2) const |
| Assemble the the "jacobian" matrix of second derivatives of the mapping from local to Eulerian coordinates, given the second derivatives of the shape functions w.r.t. local coordinates. | |
| virtual void | assemble_eulerian_base_vectors (const DShape &dpsids, DenseMatrix< double > &interpolated_G) const |
| Assemble the covariant Eulerian base vectors, assuming that the derivatives of the shape functions with respect to the local coordinates have already been constructed. | |
| template<unsigned DIM> | |
| double | invert_jacobian (const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, DenseMatrix< double > &inverse_jacobian) const |
| Take the matrix passed as jacobian and return its inverse in inverse_jacobian. This function is templated by the dimension of the element because matrix inversion cannot be written efficiently in a generic manner. | |
| virtual double | invert_jacobian_mapping (const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, DenseMatrix< double > &inverse_jacobian) const |
| A template-free interface that takes the matrix passed as jacobian and return its inverse in inverse_jacobian. By default the function will use the dimension of the element to call the correct invert_jacobian(..) function. This should be overloaded for efficiency (removal of a switch statement) in specific elements. | |
| virtual double | local_to_eulerian_mapping (const DShape &dpsids, DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, DenseMatrix< double > &inverse_jacobian) const |
| Calculate the mapping from local to Eulerian coordinates, given the derivatives of the shape functions w.r.t. local coordinates. Returns the determinant of the jacobian, the jacobian and inverse jacobian. | |
| double | local_to_eulerian_mapping (const DShape &dpsids, DenseMatrix< double > &inverse_jacobian) const |
| Calculate the mapping from local to Eulerian coordinates, given the derivatives of the shape functions w.r.t. local coordinates, Return only the determinant of the jacobian and the inverse of the mapping (ds/dx). | |
| virtual double | local_to_eulerian_mapping_diagonal (const DShape &dpsids, DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, DenseMatrix< double > &inverse_jacobian) const |
| Calculate the mapping from local to Eulerian coordinates given the derivatives of the shape functions w.r.t the local coordinates. assuming that the coordinates are aligned in the direction of the local coordinates, i.e. there are no cross terms and the jacobian is diagonal. This function returns the determinant of the jacobian, the jacobian and the inverse jacobian. | |
| virtual void | dJ_eulerian_dnodal_coordinates (const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, const DShape &dpsids, DenseMatrix< double > &djacobian_dX) const |
| A template-free interface that calculates the derivative of the jacobian of a mapping with respect to the nodal coordinates X_ij. To do this it requires the jacobian matrix and the derivatives of the shape functions w.r.t. the local coordinates. By default the function will use the dimension of the element to call the correct dJ_eulerian_dnodal_coordinates_templated_helper(..) function. This should be overloaded for efficiency (removal of a switch statement) in specific elements. | |
| template<unsigned DIM> | |
| void | dJ_eulerian_dnodal_coordinates_templated_helper (const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, const DShape &dpsids, DenseMatrix< double > &djacobian_dX) const |
| Calculate the derivative of the jacobian of a mapping with respect to the nodal coordinates X_ij using the jacobian matrix and the derivatives of the shape functions w.r.t. the local coordinates. This function is templated by the dimension of the element. | |
| virtual void | d_dshape_eulerian_dnodal_coordinates (const double &det_jacobian, const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, const DenseMatrix< double > &djacobian_dX, const DenseMatrix< double > &inverse_jacobian, const DShape &dpsids, RankFourTensor< double > &d_dpsidx_dX) const |
| A template-free interface that calculates the derivative w.r.t. the nodal coordinates | |
| template<unsigned DIM> | |
| void | d_dshape_eulerian_dnodal_coordinates_templated_helper (const double &det_jacobian, const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, const DenseMatrix< double > &djacobian_dX, const DenseMatrix< double > &inverse_jacobian, const DShape &dpsids, RankFourTensor< double > &d_dpsidx_dX) const |
| Calculate the derivative w.r.t. the nodal coordinates | |
| virtual void | transform_derivatives (const DenseMatrix< double > &inverse_jacobian, DShape &dbasis) const |
| Convert derivative w.r.t.local coordinates to derivatives w.r.t the coordinates used to assemble the inverse_jacobian passed in the mapping. On entry, dbasis must contain the basis function derivatives w.r.t. the local coordinates; it will contain the derivatives w.r.t. the new coordinates on exit. This is virtual so that it may be overloaded if desired for efficiency reasons. | |
| void | transform_derivatives_diagonal (const DenseMatrix< double > &inverse_jacobian, DShape &dbasis) const |
| Convert derivative w.r.t local coordinates to derivatives w.r.t the coordinates used to assemble the inverse jacobian passed in the mapping, assuming that the coordinates are aligned in the direction of the local coordinates. On entry dbasis must contain the derivatives of the basis functions w.r.t. the local coordinates; it will contain the derivatives w.r.t. the new coordinates. are converted into the new using the mapping inverse_jacobian. | |
| virtual void | transform_second_derivatives (const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, const DenseMatrix< double > &inverse_jacobian, const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian2, DShape &dbasis, DShape &d2basis) const |
| Convert derivatives and second derivatives w.r.t. local coordiantes to derivatives and second derivatives w.r.t. the coordinates used to assemble the jacobian, inverse jacobian and jacobian2 passed to the function. By default this function will call transform_second_derivatives_template<>(...) using the dimension of the element as the template parameter. It is virtual so that it can be overloaded by a specific element to save using a switch statement. Optionally, the element writer may wish to use the transform_second_derivatives_diagonal<>(...) function On entry dbasis and d2basis must contain the derivatives w.r.t. the local coordinates; on exit they will be the derivatives w.r.t. the transformed coordinates. | |
| template<unsigned DIM> | |
| void | transform_second_derivatives_template (const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, const DenseMatrix< double > &inverse_jacobian, const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian2, DShape &dbasis, DShape &d2basis) const |
| Convert derivatives and second derivatives w.r.t. local coordinates to derivatives and second derivatives w.r.t. the coordinates used to asssmble the jacobian, inverse jacobian and jacobian2 passed in the mapping. This is templated by dimension because the method of calculation varies significantly with the dimension. On entry dbasis and d2basis must contain the derivatives w.r.t. the local coordinates; on exit they will be the derivatives w.r.t. the transformed coordinates. | |
| template<unsigned DIM> | |
| void | transform_second_derivatives_diagonal (const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, const DenseMatrix< double > &inverse_jacobian, const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian2, DShape &dbasis, DShape &d2basis) const |
| Convert derivatives and second derivatives w.r.t. local coordinates to derivatives and second derivatives w.r.t. the coordinates used to asssmble the jacobian, inverse jacobian and jacobian2 passed in the mapping. This version of the function assumes that the local coordinates are aligned with the global coordinates, i.e. the jacobians are diagonal On entry dbasis and d2basis must contain the derivatives w.r.t. the local coordinates; on exit they will be the derivatives w.r.t. the transformed coordinates. | |
| virtual void | fill_in_jacobian_from_nodal_by_fd (Vector< double > &residuals, DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian) |
| Calculate the contributions to the jacobian from the nodal degrees of freedom using finite differences. This version of the function assumes that the residuals vector has already been calculated. | |
| void | fill_in_jacobian_from_nodal_by_fd (DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian) |
| Calculate the contributions to the jacobian from the nodal degrees of freedom using finite differences. This version computes the residuals vector before calculating the jacobian terms. | |
| virtual void | update_before_nodal_fd () |
| Function that is called before the finite differencing of any nodal data. This may be overloaded to update any dependent data before finite differencing takes place. | |
| virtual void | reset_after_nodal_fd () |
| Function that is call after the finite differencing of the nodal data. This may be overloaded to reset any dependent variables that may have changed during the finite differencing. | |
| virtual void | update_in_nodal_fd (const unsigned &i) |
| Function called within the finite difference loop for nodal data after a change in the i-th nodal value. | |
| virtual void | reset_in_nodal_fd (const unsigned &i) |
| Function called within the finite difference loop for nodal data after the i-th nodal values is reset. The default behaviour is to call the update function. | |
| void | fill_in_contribution_to_jacobian (Vector< double > &residuals, DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian) |
| Add the elemental contribution to the jacobian matrix. and the residuals vector. Note that this function will NOT initialise the residuals vector or the jacobian matrix. It must be called after the residuals vector and jacobian matrix have been initialised to zero. The default is to use finite differences to calculate the jacobian. | |
| template<> | |
| double | invert_jacobian (const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, DenseMatrix< double > &inverse_jacobian) const |
| Zero-d specialisation of function to calculate inverse of jacobian mapping. | |
| template<> | |
| double | invert_jacobian (const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, DenseMatrix< double > &inverse_jacobian) const |
| One-d specialisation of function to calculate inverse of jacobian mapping. | |
| template<> | |
| double | invert_jacobian (const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, DenseMatrix< double > &inverse_jacobian) const |
| Two-d specialisation of function to calculate inverse of jacobian mapping. | |
| template<> | |
| double | invert_jacobian (const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, DenseMatrix< double > &inverse_jacobian) const |
| Three-d specialisation of function to calculate inverse of jacobian mapping. | |
| template<> | |
| void | dJ_eulerian_dnodal_coordinates_templated_helper (const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, const DShape &dpsids, DenseMatrix< double > &djacobian_dX) const |
| Zero-d specialisation of function to calculate the derivative of the jacobian of a mapping with respect to the nodal coordinates X_ij. | |
| template<> | |
| void | dJ_eulerian_dnodal_coordinates_templated_helper (const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, const DShape &dpsids, DenseMatrix< double > &djacobian_dX) const |
| One-d specialisation of function to calculate the derivative of the jacobian of a mapping with respect to the nodal coordinates X_ij. | |
| template<> | |
| void | dJ_eulerian_dnodal_coordinates_templated_helper (const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, const DShape &dpsids, DenseMatrix< double > &djacobian_dX) const |
| Two-d specialisation of function to calculate the derivative of the jacobian of a mapping with respect to the nodal coordinates X_ij. | |
| template<> | |
| void | dJ_eulerian_dnodal_coordinates_templated_helper (const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, const DShape &dpsids, DenseMatrix< double > &djacobian_dX) const |
| Three-d specialisation of function to calculate the derivative of the jacobian of a mapping with respect to the nodal coordinates X_ij. | |
| template<> | |
| void | d_dshape_eulerian_dnodal_coordinates_templated_helper (const double &det_jacobian, const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, const DenseMatrix< double > &djacobian_dX, const DenseMatrix< double > &inverse_jacobian, const DShape &dpsids, RankFourTensor< double > &d_dpsidx_dX) const |
| Zero-d specialisation of function to calculate the derivative w.r.t. the nodal coordinates | |
| template<> | |
| void | d_dshape_eulerian_dnodal_coordinates_templated_helper (const double &det_jacobian, const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, const DenseMatrix< double > &djacobian_dX, const DenseMatrix< double > &inverse_jacobian, const DShape &dpsids, RankFourTensor< double > &d_dpsidx_dX) const |
| One-d specialisation of function to calculate the derivative w.r.t. the nodal coordinates | |
| template<> | |
| void | d_dshape_eulerian_dnodal_coordinates_templated_helper (const double &det_jacobian, const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, const DenseMatrix< double > &djacobian_dX, const DenseMatrix< double > &inverse_jacobian, const DShape &dpsids, RankFourTensor< double > &d_dpsidx_dX) const |
| Two-d specialisation of function to calculate the derivative w.r.t. the nodal coordinates | |
| template<> | |
| void | d_dshape_eulerian_dnodal_coordinates_templated_helper (const double &det_jacobian, const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, const DenseMatrix< double > &djacobian_dX, const DenseMatrix< double > &inverse_jacobian, const DShape &dpsids, RankFourTensor< double > &d_dpsidx_dX) const |
| Three-d specialisation of function to calculate the derivative w.r.t. the nodal coordinates | |
| template<> | |
| void | transform_second_derivatives_template (const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, const DenseMatrix< double > &inverse_jacobian, const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian2, DShape &dbasis, DShape &d2basis) const |
| Convert derivatives and second derivatives w.r.t local coordinates to derivatives w.r.t. the coordinates used to assemble the jacobian, inverse_jacobian and jacobian 2 passed. This must be specialised for each dimension, otherwise it gets very ugly Specialisation to one dimension. | |
| template<> | |
| void | transform_second_derivatives_template (const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, const DenseMatrix< double > &inverse_jacobian, const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian2, DShape &dbasis, DShape &d2basis) const |
| Convert derivatives and second derivatives w.r.t local coordinates to derivatives w.r.t. the coordinates used to assemble the jacobian, inverse_jacobian and jacobian 2 passed. This must be specialised for each dimension, otherwise it gets very ugly. Specialisation to two spatial dimensions. | |
| template<> | |
| void | transform_second_derivatives_diagonal (const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, const DenseMatrix< double > &inverse_jacobian, const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian2, DShape &dbasis, DShape &d2basis) const |
| Convert derivatives and second derivatives w.r.t local coordinates to derivatives w.r.t. the coordinates used to assemble the jacobian, inverse_jacobian and jacobian 2 passed. This must be specialised for each dimension, otherwise it gets very ugly Specialisation to one dimension. | |
| template<> | |
| void | transform_second_derivatives_diagonal (const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, const DenseMatrix< double > &inverse_jacobian, const DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian2, DShape &dbasis, DShape &d2basis) const |
| Convert second derivatives w.r.t. local coordinates to second derivatives w.r.t. the coordinates passed in the tensor coordinate. Specialised to two spatial dimension. | |
 Protected Member Functions inherited from oomph::GeneralisedElement Protected Member Functions inherited from oomph::GeneralisedElement | |
| unsigned | add_internal_data (Data *const &data_pt, const bool &fd=true) |
Add a (pointer to an) internal data object to the element and return the index required to obtain it from the access function internal_data_pt(). The boolean indicates whether the datum should be included in the general finite-difference loop when calculating the jacobian. The default value is true, i.e. the data will be included in the finite differencing. | |
| bool | internal_data_fd (const unsigned &i) const |
| Return the status of the boolean flag indicating whether the internal data is included in the finite difference loop. | |
| void | exclude_internal_data_fd (const unsigned &i) |
| Set the boolean flag to exclude the internal datum from the finite difference loop when computing the jacobian matrix. | |
| void | include_internal_data_fd (const unsigned &i) |
| Set the boolean flag to include the internal datum in the finite difference loop when computing the jacobian matrix. | |
| void | clear_global_eqn_numbers () |
| Clear the storage for the global equation numbers and pointers to dofs (if stored) | |
| void | add_global_eqn_numbers (std::deque< unsigned long > const &global_eqn_numbers, std::deque< double * > const &global_dof_pt) |
| Add the contents of the queue global_eqn_numbers to the local storage for the local-to-global translation scheme. It is essential that the entries in the queue are added IN ORDER i.e. from the front. | |
| virtual void | assign_internal_and_external_local_eqn_numbers (const bool &store_local_dof_pt) |
| Assign the local equation numbers for the internal and external Data This must be called after the global equation numbers have all been assigned. It is virtual so that it can be overloaded by ElementWithExternalElements so that any external data from the external elements in included in the numbering scheme. If the boolean argument is true then pointers to the dofs will be stored in Dof_pt. | |
| virtual void | assign_additional_local_eqn_numbers () |
| Setup any additional look-up schemes for local equation numbers. Examples of use include using local storage to refer to explicit degrees of freedom. The additional memory cost of such storage may or may not be offset by fast local access. | |
| int | internal_local_eqn (const unsigned &i, const unsigned &j) const |
| Return the local equation number corresponding to the j-th value stored at the i-th internal data. | |
| int | external_local_eqn (const unsigned &i, const unsigned &j) |
| Return the local equation number corresponding to the j-th value stored at the i-th external data. | |
| void | fill_in_jacobian_from_internal_by_fd (Vector< double > &residuals, DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, const bool &fd_all_data=false) |
| Calculate the contributions to the jacobian from the internal degrees of freedom using finite differences. This version of the function assumes that the residuals vector has already been calculated. If the boolean argument is true, the finite differencing will be performed for all internal data, irrespective of the information in Data_fd. The default value (false) uses the information in Data_fd to selectively difference only certain data. | |
| void | fill_in_jacobian_from_internal_by_fd (DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, const bool &fd_all_data=false) |
| Calculate the contributions to the jacobian from the internal degrees of freedom using finite differences. This version computes the residuals vector before calculating the jacobian terms. If the boolean argument is true, the finite differencing will be performed for all internal data, irrespective of the information in Data_fd. The default value (false) uses the information in Data_fd to selectively difference only certain data. | |
| void | fill_in_jacobian_from_external_by_fd (Vector< double > &residuals, DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, const bool &fd_all_data=false) |
| Calculate the contributions to the jacobian from the external degrees of freedom using finite differences. This version of the function assumes that the residuals vector has already been calculated. If the boolean argument is true, the finite differencing will be performed for all external data, irrespective of the information in Data_fd. The default value (false) uses the information in Data_fd to selectively difference only certain data. | |
| void | fill_in_jacobian_from_external_by_fd (DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, const bool &fd_all_data=false) |
| Calculate the contributions to the jacobian from the external degrees of freedom using finite differences. This version computes the residuals vector before calculating the jacobian terms. If the boolean argument is true, the finite differencing will be performed for all internal data, irrespective of the information in Data_fd. The default value (false) uses the information in Data_fd to selectively difference only certain data. | |
| virtual void | update_before_internal_fd () |
| Function that is called before the finite differencing of any internal data. This may be overloaded to update any dependent data before finite differencing takes place. | |
| virtual void | reset_after_internal_fd () |
| Function that is call after the finite differencing of the internal data. This may be overloaded to reset any dependent variables that may have changed during the finite differencing. | |
| virtual void | update_in_internal_fd (const unsigned &i) |
| Function called within the finite difference loop for internal data after a change in any values in the i-th internal data object. | |
| virtual void | reset_in_internal_fd (const unsigned &i) |
| Function called within the finite difference loop for internal data after the values in the i-th external data object are reset. The default behaviour is to call the update function. | |
| virtual void | update_before_external_fd () |
| Function that is called before the finite differencing of any external data. This may be overloaded to update any dependent data before finite differencing takes place. | |
| virtual void | reset_after_external_fd () |
| Function that is call after the finite differencing of the external data. This may be overloaded to reset any dependent variables that may have changed during the finite differencing. | |
| virtual void | update_in_external_fd (const unsigned &i) |
| Function called within the finite difference loop for external data after a change in any values in the i-th external data object. | |
| virtual void | reset_in_external_fd (const unsigned &i) |
| Function called within the finite difference loop for external data after the values in the i-th external data object are reset. The default behaviour is to call the update function. | |
| virtual void | fill_in_contribution_to_mass_matrix (Vector< double > &residuals, DenseMatrix< double > &mass_matrix) |
| Add the elemental contribution to the mass matrix matrix. and the residuals vector. Note that this function should NOT initialise the residuals vector or the mass matrix. It must be called after the residuals vector and jacobian matrix have been initialised to zero. The default is deliberately broken. | |
| virtual void | fill_in_contribution_to_jacobian_and_mass_matrix (Vector< double > &residuals, DenseMatrix< double > &jacobian, DenseMatrix< double > &mass_matrix) |
| Add the elemental contribution to the jacobian matrix, mass matrix and the residuals vector. Note that this function should NOT initialise any entries. It must be called after the residuals vector and matrices have been initialised to zero. | |
| virtual void | fill_in_contribution_to_dresiduals_dparameter (double *const ¶meter_pt, Vector< double > &dres_dparam) |
| Add the elemental contribution to the derivatives of the residuals with respect to a parameter. This function should NOT initialise any entries and must be called after the entries have been initialised to zero The default implementation is to use finite differences to calculate the derivatives. | |
| virtual void | fill_in_contribution_to_djacobian_dparameter (double *const ¶meter_pt, Vector< double > &dres_dparam, DenseMatrix< double > &djac_dparam) |
| Add the elemental contribution to the derivatives of the elemental Jacobian matrix and residuals with respect to a parameter. This function should NOT initialise any entries and must be called after the entries have been initialised to zero The default implementation is to use finite differences to calculate the derivatives. | |
| virtual void | fill_in_contribution_to_djacobian_and_dmass_matrix_dparameter (double *const ¶meter_pt, Vector< double > &dres_dparam, DenseMatrix< double > &djac_dparam, DenseMatrix< double > &dmass_matrix_dparam) |
| Add the elemental contribution to the derivative of the jacobian matrix, mass matrix and the residuals vector with respect to the passed parameter. Note that this function should NOT initialise any entries. It must be called after the residuals vector and matrices have been initialised to zero. | |
| virtual void | fill_in_contribution_to_hessian_vector_products (Vector< double > const &Y, DenseMatrix< double > const &C, DenseMatrix< double > &product) |
| Fill in contribution to the product of the Hessian (derivative of Jacobian with respect to all variables) an eigenvector, Y, and other specified vectors, C (d(J_{ij})/d u_{k}) Y_{j} C_{k}. | |
| virtual void | fill_in_contribution_to_inner_products (Vector< std::pair< unsigned, unsigned > > const &history_index, Vector< double > &inner_product) |
| Fill in the contribution to the inner products between given pairs of history values. | |
| virtual void | fill_in_contribution_to_inner_product_vectors (Vector< unsigned > const &history_index, Vector< Vector< double > > &inner_product_vector) |
| Fill in the contributions to the vectors that when taken as dot product with other history values give the inner product over the element. | |
Protected Attributes | |
| Vector< unsigned > | P_linearised_nst_internal_index |
| Internal indices that indicate at which internal data the pressure values are stored. We note that there are two pressure values, corresponding to the functions P^C(r,z,t) and P^S(r,z,t) which multiply the cosine and sine terms respectively. | |
 Protected Attributes inherited from oomph::LinearisedNavierStokesEquations Protected Attributes inherited from oomph::LinearisedNavierStokesEquations | |
| double * | Viscosity_Ratio_pt |
| Pointer to the viscosity ratio (relative to the viscosity used in the definition of the Reynolds number) | |
| double * | Density_Ratio_pt |
| Pointer to the density ratio (relative to the density used in the definition of the Reynolds number) | |
| double * | Re_pt |
| Pointer to global Reynolds number. | |
| double * | ReSt_pt |
| Pointer to global Reynolds number x Strouhal number (=Womersley) | |
| double * | Lambda_pt |
| Pointer to eigenvalue. | |
| double * | Omega_pt |
| Pointer to frequency. | |
| LinearisedNavierStokesEigenfunctionNormalisationElement * | Normalisation_element_pt |
| Pointer to the normalisation element. | |
| unsigned | Data_number_of_eigenvalue |
| Index of datum where eigenvalue is stored. | |
| unsigned | Index_of_eigenvalue |
| void(* | Base_flow_u_fct_pt )(const double &time, const Vector< double > &x, Vector< double > &result) |
| Pointer to base flow solution (velocity components) function. | |
| void(* | Base_flow_dudx_fct_pt )(const double &time, const Vector< double > &x, DenseMatrix< double > &result) |
| Pointer to derivatives of base flow solution velocity components w.r.t. global coordinates (r and z) function. | |
| bool | ALE_is_disabled |
| Boolean flag to indicate if ALE formulation is disabled when the time-derivatives are computed. Only set to true if you're sure that the mesh is stationary. | |
 Protected Attributes inherited from oomph::FiniteElement Protected Attributes inherited from oomph::FiniteElement | |
| MacroElement * | Macro_elem_pt |
| Pointer to the element's macro element (NULL by default) | |
 Protected Attributes inherited from oomph::GeneralisedElement Protected Attributes inherited from oomph::GeneralisedElement | |
| int | Non_halo_proc_ID |
| Non-halo processor ID for Data; -1 if it's not a halo. | |
| bool | Must_be_kept_as_halo |
| Does this element need to be kept as a halo element during a distribute? | |
 Protected Attributes inherited from oomph::GeomObject Protected Attributes inherited from oomph::GeomObject | |
| unsigned | NLagrangian |
| Number of Lagrangian (intrinsic) coordinates. | |
| unsigned | Ndim |
| Number of Eulerian coordinates. | |
| TimeStepper * | Geom_object_time_stepper_pt |
| Timestepper (used to handle access to geometry at previous timesteps) | |
Static Private Attributes | |
| static const unsigned | Initial_Nvalue [] |
| Static array of ints to hold required number of variables at nodes. | |
Additional Inherited Members | |
 Public Types inherited from oomph::FiniteElement Public Types inherited from oomph::FiniteElement | |
| typedef void(* | SteadyExactSolutionFctPt) (const Vector< double > &, Vector< double > &) |
| Function pointer for function that computes vector-valued steady "exact solution" | |
| typedef void(* | UnsteadyExactSolutionFctPt) (const double &, const Vector< double > &, Vector< double > &) |
| Function pointer for function that computes Vector-valued time-dependent function | |
 Public Attributes inherited from oomph::LinearisedNavierStokesEquations Public Attributes inherited from oomph::LinearisedNavierStokesEquations | |
| void(*&)(const double &time, const Vector< double > &x, Vector< double > &f) | base_flow_u_fct_pt () |
| Access function for the base flow solution pointer. | |
| void(*&)(const double &time, const Vector< double > &x, DenseMatrix< double > &f) | base_flow_dudx_fct_pt () |
| Access function for the derivatives of the base flow w.r.t. global coordinates solution pointer. | |
 Static Public Attributes inherited from oomph::LinearisedNavierStokesEquations Static Public Attributes inherited from oomph::LinearisedNavierStokesEquations | |
| static Vector< double > | Gamma |
| Vector to decide whether the stress-divergence form is used or not. | |
 Static Public Attributes inherited from oomph::FiniteElement Static Public Attributes inherited from oomph::FiniteElement | |
| static double | Tolerance_for_singular_jacobian = 1.0e-16 |
| Tolerance below which the jacobian is considered singular. | |
| static bool | Accept_negative_jacobian = false |
| Boolean that if set to true allows a negative jacobian in the transform between global and local coordinates (negative surface area = left-handed coordinate system). | |
| static bool | Suppress_output_while_checking_for_inverted_elements |
| Static boolean to suppress output while checking for inverted elements. | |
 Static Public Attributes inherited from oomph::GeneralisedElement Static Public Attributes inherited from oomph::GeneralisedElement | |
| static bool | Suppress_warning_about_any_repeated_data = false |
| Static boolean to suppress warnings about repeated data. Defaults to false. | |
| static bool | Suppress_warning_about_repeated_internal_data |
| Static boolean to suppress warnings about repeated internal data. Defaults to false. | |
| static bool | Suppress_warning_about_repeated_external_data = true |
| Static boolean to suppress warnings about repeated external data. Defaults to true. | |
| static double | Default_fd_jacobian_step = 1.0e-8 |
| Double used for the default finite difference step in elemental jacobian calculations. | |
 Static Protected Attributes inherited from oomph::FiniteElement Static Protected Attributes inherited from oomph::FiniteElement | |
| static const unsigned | Default_Initial_Nvalue = 0 |
| Default return value for required_nvalue(n) which gives the number of "data" values required by the element at node n; for example, solving a Poisson equation would required only one "data" value at each node. The defaults is set to zero, because a general element is problem-less. | |
| static const double | Node_location_tolerance = 1.0e-14 |
| Default value for the tolerance to be used when locating nodes via local coordinates. | |
| static const unsigned | N2deriv [] = {0, 1, 3, 6} |
| Static array that holds the number of second derivatives as a function of the dimension of the element. | |
 Static Protected Attributes inherited from oomph::GeneralisedElement Static Protected Attributes inherited from oomph::GeneralisedElement | |
| static DenseMatrix< double > | Dummy_matrix |
| Empty dense matrix used as a dummy argument to combined residual and jacobian functions in the case when only the residuals are being assembled. | |
| static std::deque< double * > | Dof_pt_deque |
| Static storage for deque used to add_global_equation_numbers when pointers to the dofs in each element are not required. | |
Detailed Description
Crouzeix-Raviart elements are Navier-Stokes elements with quadratic interpolation for velocities and positions, but a discontinuous linear pressure interpolation.
Definition at line 594 of file linearised_navier_stokes_elements.h.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ LinearisedQCrouzeixRaviartElement()
|
inline |
Constructor: there are three internal values for each of the two pressure components.
Definition at line 642 of file linearised_navier_stokes_elements.h.
References oomph::GeneralisedElement::add_internal_data(), i, and P_linearised_nst_internal_index.
Member Function Documentation
◆ copy_efunction_to_normalisation()
|
inline |
Definition at line 723 of file linearised_navier_stokes_elements.h.
References i, oomph::GeneralisedElement::internal_data_pt(), oomph::FiniteElement::nnode(), and oomph::FiniteElement::node_pt().
◆ dshape_and_dtest_eulerian_at_knot_linearised_nst()
|
inlineprotectedvirtual |
Velocity shape and test functions and their derivatives w.r.t. global coordinates at the ipt-th integation point (taken from geometry). Return Jacobian of mapping between local and global coordinates.
Derivatives of the shape functions and test functions w.r.t. global (Eulerian) coordinates at the ipt-th integration point. Return Jacobian of mapping between local and global coordinates.
Implements oomph::LinearisedNavierStokesEquations.
Definition at line 845 of file linearised_navier_stokes_elements.h.
References oomph::FiniteElement::dshape_eulerian_at_knot().
◆ dshape_and_dtest_eulerian_linearised_nst()
|
inlineprotectedvirtual |
Velocity shape and test functions and their derivatives w.r.t. global coordinates at local coordinate s (taken from geometry). Return Jacobian of mapping between local and global coordinates.
Derivatives of the shape functions and test functions w.r.t. global (Eulerian) coordinates at local coordinate s. Return Jacobian of mapping between local and global coordinates.
Implements oomph::LinearisedNavierStokesEquations.
Definition at line 824 of file linearised_navier_stokes_elements.h.
References oomph::FiniteElement::dshape_eulerian().
◆ fix_pressure()
|
inline |
Fix both components of the internal pressure degrees of freedom p_dof to pvalue.
Definition at line 764 of file linearised_navier_stokes_elements.h.
References i, oomph::GeneralisedElement::internal_data_pt(), P_linearised_nst_internal_index, oomph::Data::pin(), and oomph::Data::set_value().
◆ ndof_types()
|
inlinevirtual |
The number of "dof-blocks" that degrees of freedom in this element are sub-divided into: Velocity and pressure.
Reimplemented from oomph::GeneralisedElement.
Definition at line 808 of file linearised_navier_stokes_elements.h.
◆ npres_linearised_nst()
|
inlinevirtual |
Return number of pressure values corresponding to a single pressure component.
Implements oomph::LinearisedNavierStokesEquations.
Definition at line 757 of file linearised_navier_stokes_elements.h.
Referenced by oomph::RefineableLinearisedQCrouzeixRaviartElement::unpin_elemental_pressure_dofs().
◆ output() [1/4]
Redirect output to NavierStokesEquations output.
Reimplemented from oomph::LinearisedNavierStokesEquations.
Definition at line 795 of file linearised_navier_stokes_elements.h.
References oomph::LinearisedNavierStokesEquations::output().
◆ output() [2/4]
|
inlinevirtual |
Redirect output to NavierStokesEquations output.
Reimplemented from oomph::LinearisedNavierStokesEquations.
Definition at line 801 of file linearised_navier_stokes_elements.h.
References oomph::LinearisedNavierStokesEquations::output().
◆ output() [3/4]
|
inlinevirtual |
Redirect output to NavierStokesEquations output.
Reimplemented from oomph::LinearisedNavierStokesEquations.
Definition at line 783 of file linearised_navier_stokes_elements.h.
References oomph::LinearisedNavierStokesEquations::output().
◆ output() [4/4]
|
inlinevirtual |
Redirect output to NavierStokesEquations output.
Reimplemented from oomph::LinearisedNavierStokesEquations.
Definition at line 789 of file linearised_navier_stokes_elements.h.
References oomph::LinearisedNavierStokesEquations::output().
◆ p_linearised_nst()
|
inlinevirtual |
Return the pressure value i at internal dof i_internal (Discontinous pressure interpolation – no need to cater for hanging nodes)
Implements oomph::LinearisedNavierStokesEquations.
Definition at line 664 of file linearised_navier_stokes_elements.h.
References i, oomph::GeneralisedElement::internal_data_pt(), P_linearised_nst_internal_index, and oomph::Data::value().
◆ p_local_eqn()
|
inlinevirtual |
Overload the access function for the i-th component of the pressure's local equation numbers.
Implements oomph::LinearisedNavierStokesEquations.
Definition at line 777 of file linearised_navier_stokes_elements.h.
References i, oomph::GeneralisedElement::internal_local_eqn(), and P_linearised_nst_internal_index.
◆ pin_pressure_normalisation_dofs()
|
inlinevirtual |
Pin the normalisation dofs.
Implements oomph::LinearisedNavierStokesEquations.
Definition at line 671 of file linearised_navier_stokes_elements.h.
References i, oomph::GeneralisedElement::internal_data_pt(), and oomph::Data::pin_all().
◆ pin_real_or_imag()
|
inlinevirtual |
Pin the real or imaginary part of the problem Input integer 0 for real 1 for imaginary.
Implements oomph::LinearisedNavierStokesEquations.
Definition at line 679 of file linearised_navier_stokes_elements.h.
References i, oomph::GeneralisedElement::internal_data_pt(), oomph::FiniteElement::nnode(), oomph::FiniteElement::node_pt(), oomph::Data::pin(), and oomph::Data::pin_all().
◆ pshape_linearised_nst() [1/2]
|
inlineprotectedvirtual |
Compute the pressure shape functions at local coordinate s.
Pressure shape functions.
Implements oomph::LinearisedNavierStokesEquations.
Definition at line 866 of file linearised_navier_stokes_elements.h.
References s.
Referenced by pshape_linearised_nst().
◆ pshape_linearised_nst() [2/2]
|
inlineprotectedvirtual |
Compute the pressure shape and test functions at local coordinate s.
Define the pressure shape and test functions.
Implements oomph::LinearisedNavierStokesEquations.
Definition at line 877 of file linearised_navier_stokes_elements.h.
References i, pshape_linearised_nst(), and s.
◆ required_nvalue()
|
virtual |
Return number of values (pinned or dofs) required at local node n.
Number of values (pinned or dofs) required at node n.
Reimplemented from oomph::FiniteElement.
Definition at line 792 of file linearised_navier_stokes_elements.cc.
References Initial_Nvalue.
◆ unpin_real_or_imag()
|
inlinevirtual |
Implements oomph::LinearisedNavierStokesEquations.
Definition at line 701 of file linearised_navier_stokes_elements.h.
References i, oomph::GeneralisedElement::internal_data_pt(), oomph::FiniteElement::nnode(), oomph::FiniteElement::node_pt(), and oomph::Data::unpin_all().
Member Data Documentation
◆ Initial_Nvalue
Static array of ints to hold required number of variables at nodes.
Set the data for the number of variables at each node.
Linearised axisymmetric Crouzeix-Raviart elements
Definition at line 600 of file linearised_navier_stokes_elements.h.
Referenced by required_nvalue().
◆ P_linearised_nst_internal_index
|
protected |
Internal indices that indicate at which internal data the pressure values are stored. We note that there are two pressure values, corresponding to the functions P^C(r,z,t) and P^S(r,z,t) which multiply the cosine and sine terms respectively.
Definition at line 607 of file linearised_navier_stokes_elements.h.
Referenced by fix_pressure(), oomph::RefineableLinearisedQCrouzeixRaviartElement::further_build(), LinearisedQCrouzeixRaviartElement(), p_linearised_nst(), p_local_eqn(), oomph::RefineableLinearisedQCrouzeixRaviartElement::rebuild_from_sons(), and oomph::RefineableLinearisedQCrouzeixRaviartElement::unpin_elemental_pressure_dofs().
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files: